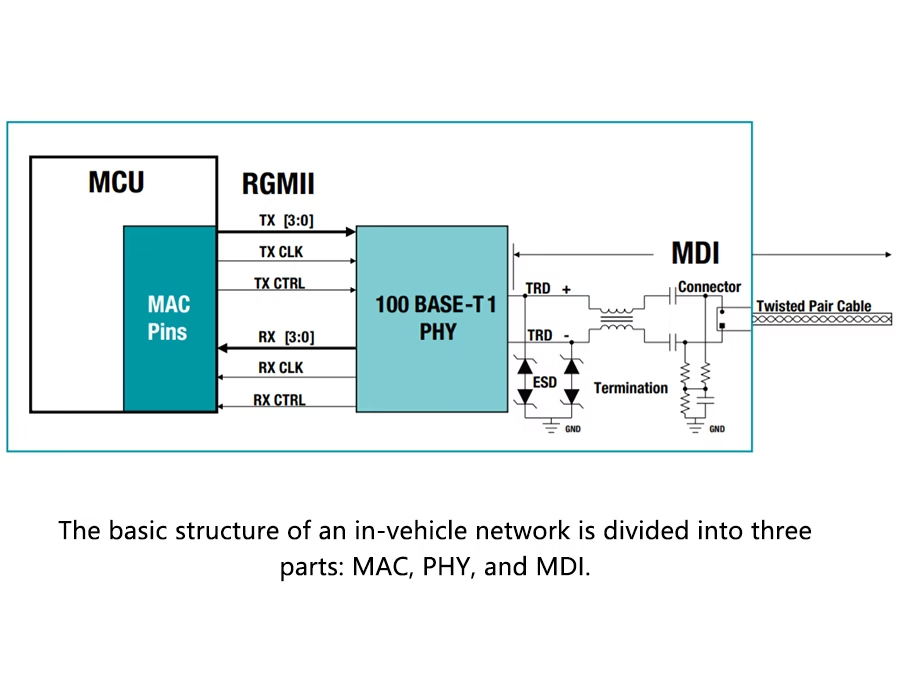
Robust wire harnesses are crucial for the reliable transmission of electricity and signals in modern automated machinery, including conveyors, robotic arms, and CNC machines. Conductors are bundled and shielded by a wire harness, allowing a machine to bend, twist, and operate constantly without malfunction.
These harnesses are exposed to extreme temperatures, grease, vibration, and electrical noise in real-world situations. Therefore, cables and connections approved for harsh use must be selected by engineers. High-end harnesses employ durable jackets (like polyurethane) and high-temperature insulations (like silicone, PTFE, or specialty polymers) to prevent degradation or melting under hot conditions.
Additionally, they are designed to meet stringent safety requirements, including IP-rated connectors for dust/water sealing, as well as flame-retardant tests (UL94 or IEC 60332). Therefore, well-made harnesses provide manufacturing floors with decades of trouble-free operation.
Connectors are used to end the bundles of insulated wires. Abrasion-resistant jackets and shields are used in conjunction with high-quality harnesses to withstand the rigors of industrial use.
Durability in Harsh Conditions
An important consideration for industrial harnesses is durability. Extreme temperatures, oils and chemicals, abrasion, and constant flexing must all be avoided. Insulating materials that withstand temperatures much above 125°C, such as silicone rubber, fluoropolymers, or PTFE (Teflon), are used in high-temperature-rated harnesses. Specific cables of aircraft quality can withstand temperatures of up to 250°C or more.
- High-Temp Insulation: At high temperatures, wires with ceramic, silicone, or PTFE jackets maintain their flexibility. Romtronic, for example, mentions harness assemblies that can withstand temperatures ranging from -65°C to +250°C. This is crucial for machinery that uses spindles or motors to generate heat.
- Oil and Chemical Resistance: Ordinary PVC insulation can be deteriorated by solvents, coolants, and industrial lubricants. Chloroprene and polyurethane (PUR) are examples of tough jackets that can withstand exposure to coolants and oils. For instance, Romtronic offers robot cables with PUR jackets that meet the DIN EN 50363-10-2 requirements for oil resistance. Coolants, bacteria, and even drilling mud are repelled by these wires, which are also free of silicone and halogen. In greasy machine conditions, wearing a PUR or Neoprene coat helps prevent swelling or cracking.
- Abrasion and Flex Fatigue: Frequently, harnesses move using robotic joints or ride on cable carriers. Extremely extended flex life is provided by flexible jacketing and fine-stranded conductors (IEC 60228 Class 5 or 6). For instance, the extreme drag-chain cable from Romtronic passed approximately 10 million alternating bend cycles at a radius of 5 times the cable diameter. The cable won’t break or crack during continuous action thanks to these ratings. To prevent internal wire fatigue, drag-chain cables also specify a minimum bend radius, typically 3 to 5 times the diameter of the cable.
Reputable wire harness manufacturers test each component for functionality, tensile strength, insulation resistance, and continuity under pressure. Through automated testing, high-quality industrial machinery harness manufacturers can detect approximately 99.7% of defects (such as loose crimps, disconnected wires, and shorts). High-voltage and forced tensile testing identify any “weak links” in a single inspection, preventing them from reaching customers. The end product is a harness that performs properly even under extreme conditions, including heat, shock, and bending.
🛠 Need wire harnesses that endure real industrial abuse?
Romtronic builds harnesses with drag-chain rated cables, high-temperature insulation, and PUR-style rugged jackets — designed to resist flex fatigue, oil, and abrasion in the harshest conditions.
📩 Contact us now for a durability-driven harness design & quote →
Safety and Compliance
Safety features protect against interference, electric shock, and fire. A single meltdown or short circuit in a machine might have disastrous consequences. To meet stringent fire safety requirements, such as UL94 V-0 or IEC 60332 flame tests, as well as regulations like NEC/NEK or DNV for marine/offshore use, harnesses incorporate flame-retardant materials and shielding. Numerous industrial cables are VW-1 (vertical flame) rated and UL/CSA listed.
- EMI/RFI Shielding: Sensor and data streams can be distorted by noise from motors, drives, and welders. Conductors are protected from electromagnetic interference by shielded wires, such as foil or braided copper shields. Filled/tinned copper shields (100% coverage foil plus braid) guarantee clean signals in industrial Ethernet or feedback loops. Shielded servo cable assemblies, for example, preserve signal integrity and avoid crosstalk even when placed next to high-current coils. (To reduce interference, industry data cables frequently employ twist-and-shield configurations.)
- Ingress Protection: Harness connectors adhere to IP standards (such as IP67) to prevent water and dust from getting into connections. O-rings or overmolds are used to seal standardized connectors, such as M12 or circular MIL-spec connectors. Molex highlights that IP67-rated M12 connectors provide “reliable … power, signal and data transmission in harsh industrial environments”. These sealed connectors can tolerate vibration and brief submersion. In actuality, selecting IP67/68 glands and plugs helps wiring withstand coolant spray or washdowns.
Reliability and Quality
The key to reliability lies in long-term, stable performance. Reliability is built on high-quality materials and meticulous assembly from the outset. The quality of the conductors within the wiring harness is crucial. Grade 5/6 finely stranded wire, 99.99% pure copper, and occasionally tinned copper for corrosion protection are essential. Tinned conductors (made of tinned copper) are often used on robots or conveyor belts to prevent oxidation.
Tinned copper prevents corrosion and extends wire life in humid, oily environments. Tinning also keeps conductors electrically clean in environments with coolant mist or salt spray.
- Connector and Termination Quality: A failure point is a broken strand or loose crimp at a terminal. Premium crimp terminals, solder junctions, or IDC fittings that have been tested for pull strength are used in industrial harnesses. To prevent corrosion, connectors are plated with nickel or gold. Fused splices or redundant pins provide additional buffer for essential circuits. Each connector features a strain-relieving mechanism to prevent wires from breaking during movement. Install problems are also eliminated by using proper labeling and color coding.
- Testing & Certification: After assembly, the harnesses undergo mechanical and electrical testing. Connectivity, insulation, and high-voltage resistance are all 100% tested by multiple suppliers. Stress tests, simulating years of use, include vibration, flexing, and thermal cycling. Early fault detection significantly improves safety and reliability, minimizing downtime costs. Leading harness manufacturers adhere to MIL, ANSI/UL, IEC, and ISO standards. For example, they employ ISO 9001 production processes, UL 1581 standards for cable flammability and flexibility, and IEC 60228 standards for conductor types.
Performance Comparison: Harness specifications should be matched to the needs of industrial users. A standard PVC cable and specialty harness cables used in robotics, drag chains, and harsh environments are contrasted in the table below:
| Feature | Standard PVC Cable | High-Flex Drag-Chain Cable | Robotic Torsion Cable | Ultra-Duty Multi-Use Cable |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Operating Temp (°C) | –20 to +80 | –40 to +80 (moving) | –40 to +90 | –30 to +90 |
| Flex Life | ~100,000 cycles | >5,000,000 cycles | ~10,000,000 (torsion) | ~10,000,000 cycles |
| Bend Radius (min) | 10× cable dia (static) | ≥5–7× dia (dynamic) | ~7× dia | 5× dia in motion |
| Jacket Material | PVC | PUR (Polyurethane) | PUR or TPU | Specialized PUR (oil/mud resist.) |
| Oil/Chemical Resistance | Low | High (oil-resistant PUR) | High (lubricant- and coolant-resistant) | Very high (drilling mud, oil) |
| Flame/Fire Rating | UL VW-1 (often) | IEC 60332/VW-1 | UL94 V0/VW-1 (robot-suit) | IEC 60332, DNV-approved |
| Shielding | Optional | Often foil+braid available | Often fully shielded pairs | Custom shielded options |
Compared to a generic PVC cable, the specialized cables (middle columns) have significantly higher flex life, oil resistance, and fire ratings. Consulting the data sheets of the manufacturers is beneficial because it guarantees that the system will satisfy the necessary industrial wire harness performance requirements through the selection of the right cable and the creation of a harness length with adequate slack.
Best Practices & Recommendations
In designing or specifying harnesses, follow these tips:
- For moving parts, use cables rated for drag chains. Robot cables are designed to withstand motion and vibration. They are often tested in drag chains and come with a lifetime guarantee (e.g., a 4-year warranty).
- Select connectors with an IP rating for exposed regions. Water and metal shavings are kept out by the IP67/68 sealed M12 and M23 connectors. In washdown zones, they make sensor and motor hookups simpler.
- Properly ground and shield. To direct noise away from delicate electronics, use grounded connectors and attach cable shields to the chassis at one end. A technique known as “EMI shielded machine cable” utilizes twist pairs and overall shields to prevent motor or VFD noise from contaminating signals.
- Utilize grommets and strain reliefs. To prevent chafing and guard against vibration fatigue, install rubber grommets or clamp fittings where the harness contacts a panel or bends around a corner.
- Clearly label the wires. Each conductor should have an ID printed or color-coded so that maintenance crews can promptly identify problems. Downtime is reduced with a well-documented harness.
- Collaborate with approved vendors. OEMs often require certifications from UL, CE, or CSA. Select suppliers who have documented quality processes (ISO 9001, IATF 16949, etc.) and demand continuity and HPT test inspection results.
With careful construction and testing, a harness made of the proper materials (such as halogen-free compounds, fine-stranded copper, and PU jackets) will provide long-lasting durability, safety, and dependability in industrial machinery.
FAQ
A: Start by measuring your machine’s maximum typical working temperature (exhaust, spindle motor, etc.). Next, include a safety margin, usually between +20 and +50 °C. For instance, use a wire rated at 125°C or 150°C if a CNC spindle operates at 80°C. These high-temperature cables use insulating materials such as ceramic tape, silicone, or PTFE.
A: Yes, however, you need to use cables that can withstand oil. In oil, a regular PVC cable will expand and break. Seek jacketing that is resistant to hydrolysis or grease. Polyurethane (PUR) jackets, which adhere to DIN EN 50363 specifications, are frequently used in hydraulic and oil environments. For information on oil immersion rates or certifications, always consult the cable specification.
A: These are ingress-protection (IP) ratings. IP67 indicates the connector is dust-tight and can survive submerged to 1 m for 30 minutes. It may be submerged deeper than 1 m (often 2–5 m) due to its IP68 rating. In actual use, IP67/68 connectors guarantee that cables remain dry during coolant sprays or washdowns. Due to their IP67 rating, Molex M12 connections and similar ones can be used in most factory settings.
A: While aluminum foil shields provide 100% coverage and perform well at higher frequencies, braided copper shields offer good mechanical strength and low-frequency noise shielding. Both an outer tinned-copper braid and an inner foil are used in many industrial cables. This guarantees extensive EMI shielding. For crucial feedback signals, servo cables, for instance, may have double shielding around each twisted pair.
A: Incorporate recurring maintenance inspections in addition to initial testing. Every year, verify insulation resistance and continuity with a cable tester or multimeter. Check connectors and jackets for noticeable wear or damage. Even in high-cycle applications where no problems manifest, cables should be replaced after a specified lifetime (in millions of cycles). Reputable vendors will include a test report or a wire harness certificate of conformance with the construction. Regular audits and catch testing (also known as wiggle testing, where connectors are tested under power) ensure the harness is trustworthy.
Durability, safety, and peace of mind are provided by each of these procedures and characteristics, which ensure your industrial wire harness operates reliably under the demanding conditions of CNCs, robots, and conveyors.
⚙️ Want industrial machinery wire harnesses that never cut corners on durability or safety?
Romtronic offers full-spec wire harnesses with high-temp insulation, drag-chain rated designs, IP-rated connectors, and flame-retardant materials — built to perform in your toughest applications.
📞 Get your custom harness quote & technical layout now →
.avif)
Sam Wu is the Marketing Manager at Romtronic, holding a degree in Mechatronics. With 12 years of experience in sales within the electronic wiring harness industry, he manages marketing efforts across Europe. An expert in cable assembly, wiring harnesses, and advanced connectivity solutions, Sam simplifies complex technologies, offering clear, actionable advice to help you confidently navigate your electrical projects.