Complex wire harnesses are essential for the secure transmission of power and data to medical devices, including surgical robots, MRI scanners, and patient monitoring systems. Engineers must fit numerous wires into confined areas, adhere to stringent safety regulations, and guarantee an incredibly dependable assembly while designing these harnesses. In this blog, we’ll examine the most challenging aspects of medical cable/harness design and offer practical solutions.
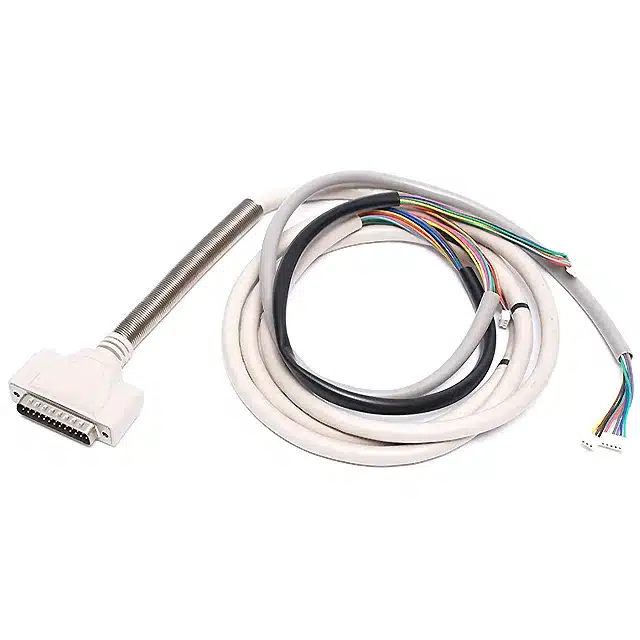



Figure: Examples of customized medical equipment wiring solutions delivered by Romtronic.
Regulatory Compliance and Safety Standards
Complying with strict medical regulations poses a significant challenge. International standards such as ISO 13485 (medical quality systems) and IEC 60601 (electrical safety of medical equipment) must be met by medical harnesses. These include everything from electrostatic discharge to insulation resistance. For example, ISO 10993 addresses biocompatibility (materials safe for skin contact), while IEC 60601-1 ensures patient safety.
Designers employ medical-grade, approved components and meticulously document each step to ensure compliance with these standards. Every wire and connector is selected or tested to satisfy UL/IEC requirements, and the manufacturing process is closely monitored. In reality, this requires thorough testing and documentation at every stage to ensure that the finished harness meets all certifications without necessitating expensive rework.
Materials and Biocompatibility
Another challenge is selecting the right materials. Medical harnesses often require biocompatibility and resistance to sterilization. Cables used in surgical settings or near patients must withstand autoclaving, chemicals, and radiation without deteriorating.
To address this, we utilize well-proven insulator materials, such as silicone and PTFE (Teflon), which withstand heat and disinfectants. At the same time, the jackets are often made of silicone or polyurethane to withstand harsh cleaners, and the wire cores are usually made of high-purity copper (for conductivity) with additional plating to prevent corrosion.
All materials are tested in accordance with ISO 10993 for skin safety, ensuring that they contain no toxins or allergens. The end product is a harness that remains flexible and safe even after numerous sterilization cycles.
Miniaturization and Space Constraints
In the case study of a compact X-ray machine, for instance, engineers required a harness to handle power, data, and controls, allowing the device to move and rotate freely. We overcame this by using CAD tools and 3D modeling to lay out the harness early. High-flex, multi-core cables can carry multiple signals in one bundle.
In the X-ray example, the team even used thinner cables and injected custom brackets to improve airflow and reduce heat. Miniaturization is a common challenge—you must pack dozens of wires into a cramped chassis without interference. Strategic routing, such as shared conduits or “zip” arrangements, also helps. In short, careful planning and innovative cabling (including hybrid bundles) solve space problems without sacrificing performance.
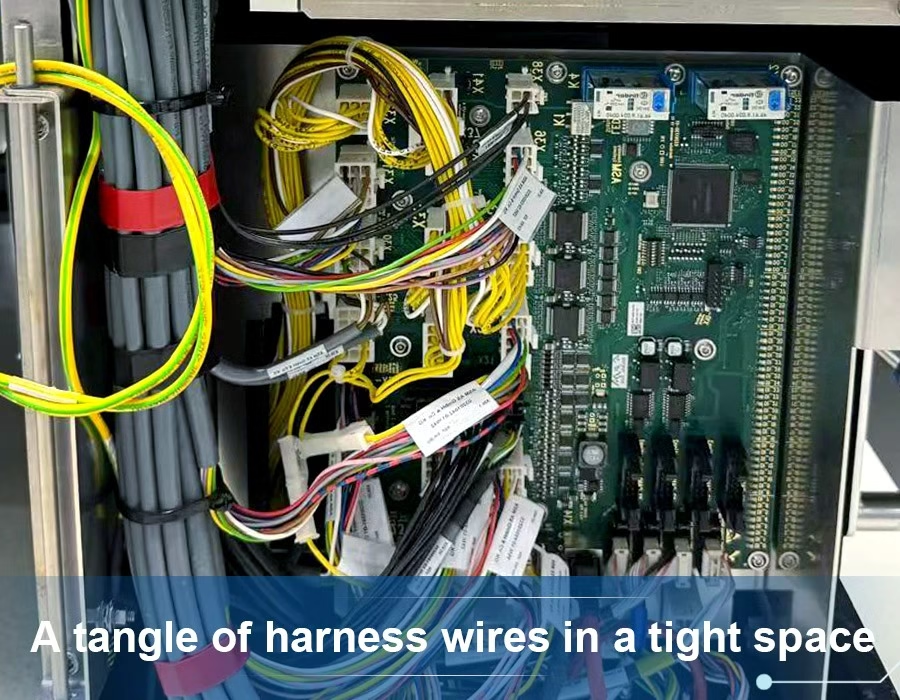
Figure: A tangle of harness wires in a tight space. Proper planning and routing are essential to avoid overheating and wear.
Signal Integrity and EMI Shielding
The hospital setting can be electrically loud, but medical harnesses need to provide precise signals. Strong electromagnetic fields produced by high-voltage imaging equipment have the potential to disrupt data connections. We employ twisted-pair architecture and shielded cable to combat electromagnetic interference, or EMI.
To safeguard high-frequency signals, MRI and CT scanners frequently use coaxial and foil-braided cables. For instance, BizLink employed multi-conductor, double-shielded cables to counteract electromagnetic interference in the X-ray case study.
Additionally, our harness designs adhere to IEC 60601-2 EMC standards. Where necessary, common-mode chokes and grounding are introduced. Just as the neatly arranged wiring under a dashboard demonstrates that every connection is intact, the attached graphic below illustrates how meticulous design ensures signals remain intact.
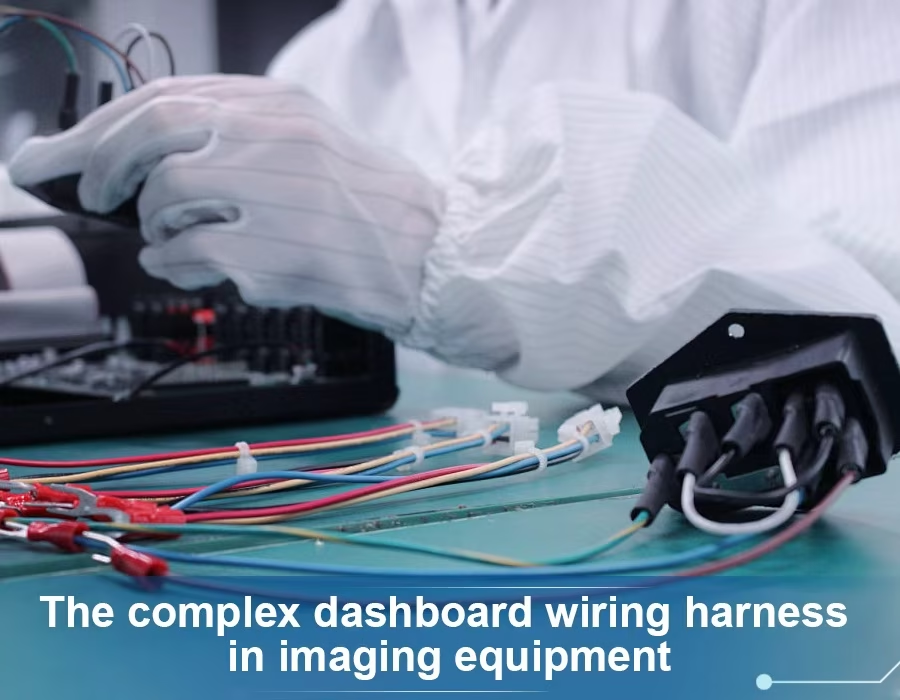
Figure: A complex dashboard harness in an imaging device. Notice the organized bundled wires and shielding used to maintain signal integrity.
Durability and Flexibility
Medical cable assemblies are subjected to severe usage. Harnesses are continuously flexed by devices such as surgical robots or handheld monitoring. Fatigue failures may occur due to repeated bending or stress if the design is not resilient. To solve this, we add strain relief and select high-flex wires. We use cables with silicone jackets or nylon braids that are rated for thousands of flex cycles, making them ideal for dynamic applications. Sharp bends are avoided with strengthened overmolds at connector ends and strain-relief boots.
Every solder junction and crimp is made to allow the insulation, not the conductor, to absorb mechanical stress. To identify weak points early in the prototyping process, we also conduct mechanical testing (such as pull and bend tests). By taking these precautions, the harness remains intact even after frequent use in the hospital.

Figure: Close-up of flexible jumper wires. In medical harnesses, using durable insulation and strain relief helps prevent breaks during motion.
Testing and Quality Assurance
The harness must be completely accurate before it is included in a gadget, regardless of how cleverly it is designed. Healthcare safety is too important to be “near enough.” From obtaining materials to carefully assembling them to conducting thorough testing, our manufacturing procedure adheres to Romtronic’s checklist. Every harness is examined several times. For instance, in accordance with IPC-A-620 regulations, we visually check wire lengths and crimp quality.
After that, we perform electrical tests to ensure there are no shorts to ground, including insulation resistance, continuity checks, and high-potential (HIPOT) testing. To identify any wiring flaws, automated harness test stations mimic signals and pass them across each cable. All of these procedures are outlined in ISO 13485 quality systems documentation.
🔧 Looking for certified and reliable medical wire harness solutions?
Romtronic delivers fully customized harnesses designed for imaging systems, surgical robots, and patient monitors—built to meet IEC 60601 and ISO 13485 standards.
📩 Contact our team today for a custom quote →
We even create or procure specialized test equipment to assist with this. Our test fixtures, for instance, can rapidly confirm the pinout of a novel harness design. QA also includes packaging and labeling, where each harness is assigned a lot number and serial code. We detect flaws before delivery and ensure dependable medical operations every time by incorporating this strict quality assurance procedure into our process.
Quick Reference: Challenges vs. Solutions
| Challenge | Solution / Best Practice |
|---|---|
| Regulatory Compliance (IEC 60601, ISO 13485, etc.) | Follow standards and document processes thoroughly |
| Material/Biocompatibility (sterilization, patient safety) | Use medical-grade PTFE/silicone materials and test per ISO 10993 |
| Space & Miniaturization | Employ CAD layouts, flexible ribbon/multi-core cables, compact custom designs |
| EMI and Signal Integrity | Add shields (foil/braid), twisted pairs, and filtering per IEC 60601-2 |
| Durability & Flex Life | Choose high-flex conductors and reinforce strain points; perform bend/pull tests |
| Manufacturing Quality | Implement one-at-a-time testing (continuity/hipot), visual IPC inspections, and traceability |
Frequently Asked Questions
A: ISO 13485 (quality management for medical devices), IEC 60601-1 (electrical safety of medical devices), and IEC 60601-2 (EMC regulations) are essential standards. Materials frequently require certification of ISO 10993 biocompatibility as well.
A: We employ insulations that can withstand high temperatures, such as silicone or PTFE (Teflon®). These materials are resistant to radiation and steam from autoclaves. Seals and connectors are also chosen to withstand cleaning solvents. Lastly, multiple sterilization cycle tests are used to validate each design.
A: We add shielding to power and data wires. Interference is captured by coaxial structures or shields made of foil and braid. Noise is eliminated using twisted pairs. Analog and digital cables may also be separated via the harness arrangement. All of this complies with EMC standards such as IEC 60601-2.
A: According to IPC-A-620, each harness undergoes visual inspection, electrical testing (continuity, insulation resistance, and high-pot voltage), and functional testing with test jigs. Every test is frequently documented in a batch log. Before assembling any medical device, potential failure modes, such as openings, shorts, or miswires, are identified and addressed.
A: The safety of the patients is at stake. Life-critical equipment can malfunction due to even a minor wiring fault. For this reason, we make investments in thorough traceability, redundant inspections, and cautious design. A well-made harness contributes to the safe and dependable use of medical equipment by patients.
Real-world applications have validated each of these solutions. For instance, engineers have successfully modified X-ray machine harnesses to eliminate EMI and overheating issues by utilizing specialized shielding and airflow control. In a separate instance, a robotic surgical instrument was able to maneuver thousands of times without experiencing any wire failures due to the flexible, silicone-jacketed wires.
🧩 Need quality-assured harnesses ready for medical applications?
Explore Romtronic’s product portfolio featuring biocompatible materials, EMI-shielded designs, and full traceability for safe device integration.
📘 Browse our Medical Wire Harness Products page →
The most challenging problems in medical wire harness design can be addressed with the right strategy, which combines materials science, innovative engineering, and rigorous quality assurance to produce safe, reliable, and efficient devices.
.avif)
Sam Wu is the Marketing Manager at Romtronic, holding a degree in Mechatronics. With 12 years of experience in sales within the electronic wiring harness industry, he manages marketing efforts across Europe. An expert in cable assembly, wiring harnesses, and advanced connectivity solutions, Sam simplifies complex technologies, offering clear, actionable advice to help you confidently navigate your electrical projects.


