If you’ve ever attempted to connect an automotive GPS antenna to a traditional RF device, you’ve likely realized that you need a FAKRA-to-SMA cable. These cables are intended to connect automotive connectors with standard SMA ports. This means that these cables will be helpful if you are working with automobiles, telematics systems, or even setting up testing or RF communications.
This article discusses the purpose of the FAKRA Z to SMA cable, why you would want one, how to install it properly, and why you should avoid poor installations. In other words, consider this your complete source for everything FAKRA Z to SMA.
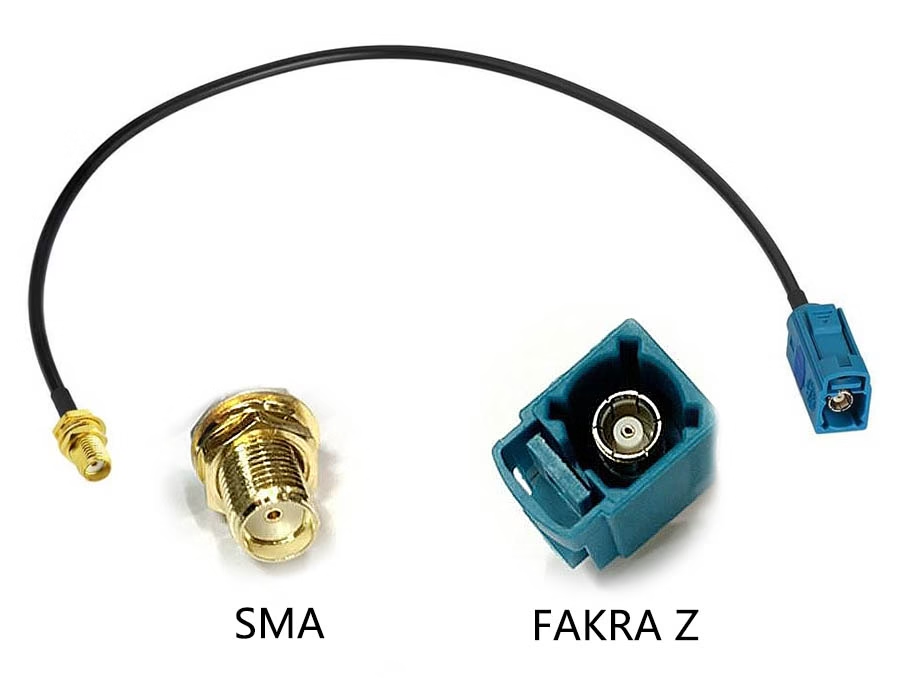
What Is a FAKRA Z Connector?
FAKRA connectors are the standard for RF connections in the automotive industry. The FAKRA Z connector has a distinctive water-blue housing. To assure a secure connection, the connector snaps into place, stays intact amid vibration, and shields against electromagnetic interference. The connectors are uniquely keyed to prevent incorrect wiring, thereby preventing catastrophes at multiple wiring points in a complex infotainment or telematics build.
You will find the FAKRA Z connector in GPS antennas, satellite radios, and other interconnect RF devices found in the interior of a vehicle. The 50-ohm impedance assures that radio signals are preserved within tolerance for the automotive application, partnered with IP67 ruggedness. Here is a fun fact: These connectors were designed to endure specific bounces, shakes, and temperature variations your car experiences every day.

What Is an SMA Connector?
Contrastingly, the SMA connector is small, threaded, and selects deliberate precision. SMA connectors are designed for high-frequency applications, such as faceplates, and are commonly found in GPS receivers, Wi-Fi devices, and RF test equipment. Male SMA has a center pin; female SMA has a sleeve. Unlike the snap-on type FAKRA, SNA connects by screwing on, permitting a secure connection.
Keep in mind that using the wrong gender or excessive torque may cause issues with the signal. A little torque goes a long way, particularly for sensitive RF applications.
Uses and Applications of FAKRA Z to SMA Cables
So, why are FAKRA Z to SMA cables required in the first place? Picture a car GPS antenna fitted with a Fakra Z plug, but your testing device or modem has a SMA input. So, without a bridge cable, you’re just not going to be able to test anything.
Examples of use cases:
- Vehicle navigation systems
- Wireless modems and testing devices
- Telematics and ADAS sensors
- Drone GPS receivers
These cables offer exceptional flexibility, reliability, and ruggedness to ensure you receive a clean RF signal, wherever you are and whatever conditions you face.
Key Specifications and Considerations
When selecting a Fakra Z to SMA cable, consider the following aspects:
- Impedance: 50 Ω to match both FAKRA and SMA systems.
- Cable type & flexibility: RG-174 or RG-316 coaxial cables are commonly used, offering flexibility to navigate tight spaces.
- Shielding: Braid or foil shielding prevents EMI from corrupting your signals.
- Connector gender: Always check Fakra and SMA ends. Male-to-male? You’ll need an adapter.
- Environment: Designed for -40 to +105°C, often IP67-rated for water resistance.
- Signal integrity: Low VSWR and insertion loss ensure your high-frequency signals remain clean.
The bottom line is that you are only as good as the quality of the cables and the reverse power of the connectors to optimize RF performance.
Installation Tips
The installation is simple, although it can be very intricate.
- The Fakra connector should latch on firmly after aligning; you should hear it click into place.
- Thread the SMA connector on just tight. Once it is hand-tight, if necessary, use a proper wrench to snug it up.
- Be cautious not to apply sharp bends; allow the excess cable to coil nicely.
- Use clips or ties to prevent stress on connectors.
- Double-check the genders: The Fakra Z male connects to a Fakra jack, and the SMA male connects to the SMA jack.
If you do all of this, your signal will continue strong for many years!
Troubleshooting Common Issues
Issues typically arise due to:
- Loose or incompatible connectors.
- Faulty wiring or inadequate shielding.
- Inadequately long/cable that causes loss of signal integrity.
- Threads on SMA connectors are getting cross-threaded.
Tip: Fakra Z is universal (Water-Blue), but always verify the connector key for your vehicle. Using the type, if you are not sure, the other match may prevent the two from mating.
Conclusion
While FAKRA Z to SMA cables are a small portion of your automotive or RF setups, they are a vital part of it. Understanding connectors, specifications, installation practices, and common mistakes will save you time, signal headaches, and money. Remember, it’s not just about the cable, it’s about the connections.
For more detailed solutions, please see our RF & Automotive Solutions page.
FAQs
A: No. You will have to use a female adapter on one end to make the connection.
A: Keep them short, usually a few inches or more, to avoid signal-loss issues.
A: The water-blue FAKRA Z will fit any FAKRA port; however, other colors/key codes may need a different adapter.
For more in-depth information on RF cables, please refer to:
- RF Cables vs. HDMI Cables: Which One Suits Your Needs?
- Introduction to RF Cable Assemblies
- RF Connector Basics: A Comprehensive Guide for High-Frequency Applications
- FAKRA Connectors: The Cornerstone of Modern Automotive Connectivity

Apple Liu is Romtronic’s Marketing Manager, focusing on business growth across the Asian market. With a background in International English and eight years of sales experience in the electronic cable and harness industry, she brings both in-depth industry knowledge and a global outlook to her role.
In addition to leading market strategy, Apple also oversees content development and editorial work—crafting clear, engaging messaging that reflects Romtronic’s values and technical strengths. She is passionate about digital engineering and is committed to strengthening Romtronic’s brand presence and innovation in a competitive global landscape.