Stable, low-loss radio-frequency (RF) connections are essential to modern vehicles, as they support navigation and connectivity and enable drivers to use intelligent/automated vehicles.
Modern vehicles utilise a wide range of interconnects for their automotive electronics; however, FAKRA Z-to-SMA cables are among the most critical components, as they connect the rugged antenna interface (vehicle side) to high-performance RF modules/testing equipment.
FAKRA Z-to-SMA Cable Assemblies do not simply adapt the signal; they are engineered RF Systems. The mechanical reliability and electrical integrity of the FAKRA Z-to-SMA Cable Assemblies affect the accuracy of GNSS, the stability of cellular networks, and the overall durability of the system.
FAKRA Z to SMA Cable Guide: An Engineering Bridge for Automotive RF Connectivity
Modern cars depend on stable, low-loss RF connections to enable Safe Navigation, Connectivity, and Sophisticated Driver Assistance Systems. Among the many interconnect products used in automotive electronics, the FAKRA Z connector-to-SMA cable solution is vital, connecting heavy-duty automotive antenna interfaces to high-performance RF modules for vehicle system testing.
FAKRA Z to SMA cable assemblies are engineered RF (radio frequency) subsystems that provide more than just a basic connection. Their mechanical reliability and electrical integrity directly affect the performance of GNSS accuracy, cellular stability, and long-term viability of a system.

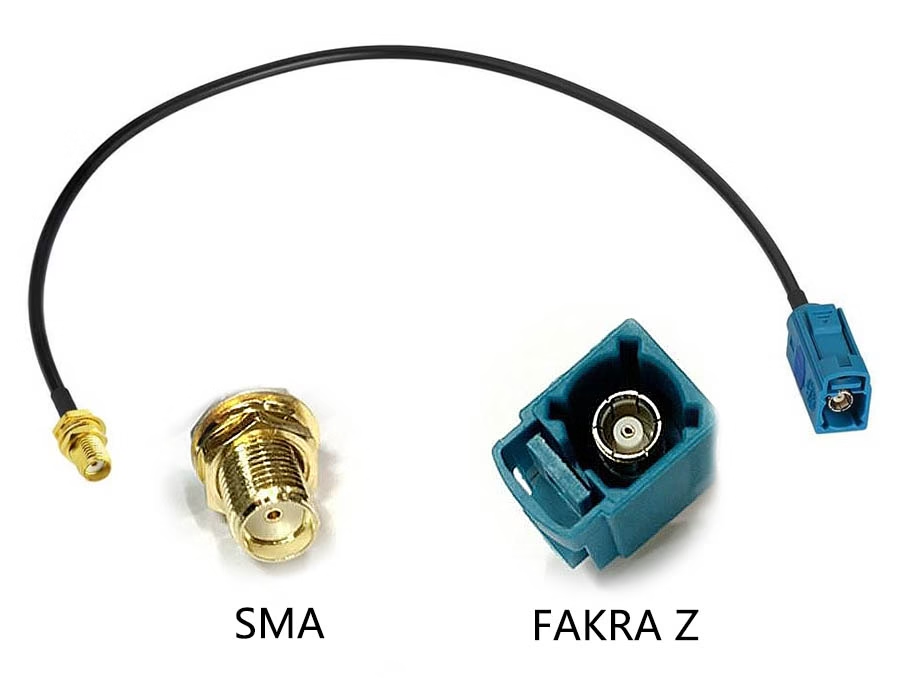
What Is a FAKRA Z to SMA Cable?
A FAKRA Z to SMA cable is a 50-ohm coaxial assembly designed to connect automotive-standard FAKRA Z interfaces with threaded SMA RF ports.
- FAKRA (Fachkreis Automobil) connectors are widely used in vehicles due to their vibration resistance, secondary locking, and color-coded mechanical keying.
- FAKRA Z is the universally keyed variant, allowing mating across FAKRA-coded systems and making it especially valuable for development, testing, repairs, and multi-signal platforms.
- SMA (SubMiniature version A) connectors are precision RF interfaces commonly used on telematics modules, GNSS receivers, cellular devices, and RF test equipment.
By bridging these two standards, FAKRA Z-to-SMA cables enable reliable RF transitions between vehicle antenna systems and internal electronic platforms.
Core Automotive Applications
FAKRA Z to SMA assemblies are most commonly deployed in three automotive RF domains:
1. GNSS and GPS Navigation
They connect roof-mounted or integrated antennas to GNSS modules, where stable impedance and shielding are essential to prevent signal reflection, positioning drift, and intermittent reception.
2. Telematics and 4G/5G Connectivity
Used extensively in TCU systems, in-vehicle hotspots, and fleet platforms, these cables support sub-6 GHz cellular bands and must tolerate vibration, temperature variation, and long routing paths.
3. Infotainment and RF-Based Vehicle Systems
Satellite radio, digital broadcast, wireless infotainment modules, and V2X platforms often rely on FAKRA-to-SMA transitions to interface standardized vehicle antenna ports with module-side RF connectors.
Technical Overview
Typical automotive-grade FAKRA Z to SMA cables are designed around the following engineering fundamentals:
- Impedance: 50 Ω controlled system
- Frequency capability: DC to 6 GHz (higher depending on connector and cable design)
- Common cable types: RG-174, RG-316, RG-58, and low-loss RF alternatives
- Shielding: single or double braided structures for EMI suppression
- Mechanical retention: quick-lock FAKRA housing and threaded SMA interface
Right-angle and straight versions are used depending on module packaging and routing constraints.
FAKRA Z vs Mini-FAKRA vs HSD vs SMA — Engineering Selection Boundaries
In automotive interconnect design, FAKRA Z is often mentioned alongside Mini-FAKRA, HSD, and SMA. Although they may appear similar, they serve very different engineering roles.
- FAKRA Z is a rugged automotive RF interface optimized for antenna and vehicle body connections. It focuses on vibration resistance, secure locking, and assembly reliability for RF signals typically up to about 6 GHz.
- Mini-FAKRA is a compact evolution of FAKRA, selected when high connector density, reduced weight, and packaging efficiency are required, such as in multi-antenna or sensor fusion modules.
- HSD (High-Speed Data) connectors are designed for high-speed digital signals such as LVDS and automotive Ethernet. They are not antenna interfaces and are not intended for RF feed lines.
- SMA connectors are precision RF interfaces widely used on RF modules, evaluation boards, and test systems. They offer strong high-frequency performance but lack the automotive locking, coding, or housing features of FAKRA systems.
Both FAKRA and Mini-FAKRA are the most commonly used connectors on the vehicle side of antenna and HSD connections for high-speed digital data links. At the same time, SMA is the most widely used connector for radio-frequency port connections and module-level testing interfaces.
The FAKRA Z-to-SMA cable was designed to connect the two connection types.
Installation and Routing Considerations
Proper installation is essential to maintaining RF integrity:
- Align the FAKRA Z connector until the audible lock confirms full engagement.
- Tighten the SMA interface to the specified torque to avoid thread damage or micro-movement.
- Respect the minimum bend radius (typically ≥5× cable diameter).
- Secure cables at defined intervals to prevent vibration-induced fatigue.
- Keep RF lines separated from high-current power paths where possible.
Post-installation RF validation, including continuity checks, insertion loss measurements, and functional signal testing, is strongly recommended.
Standard Failure Modes and Mitigation
| Symptom | Likely cause | Engineering solution |
|---|---|---|
| GNSS drift or weak signal | Impedance mismatch or shielding breakdown | Use true 50-ohm RF assemblies with verified shielding |
| Intermittent 4G/5G links | Vibration or moisture ingress | Select sealed connectors and add mechanical strain relief |
| RF noise or radio interference | Insufficient shielding | Specify double-shielded coax and validated crimp processes |
Engineering Note
A FAKRA Z to SMA cable assembly’s actual RF performance is dependent on the complete interconnect assembly, which may include connector design, coaxial cable type, assembly procedure, routing, and installation environment, plus any other components in the system, such as PCBs or enclosures. While connector frequency ratings provide guidance, they do not guarantee that a complete system will maintain signal integrity at the system level.
Engineering Decision Checklist: Specifying a FAKRA Z to SMA Cable
Before approving a FAKRA Z to SMA cable for an automotive project, engineering teams should validate the following:
- Signal definition: operating bands, bandwidth, and sensitivity
- Impedance and RF continuity: verified 50-ohm system integrity
- Cable construction: RG-174, RG-316, RG-58, or low-loss alternatives based on attenuation budget
- Mechanical environment: vibration exposure, bend radius, retention force
- Environmental resistance: temperature range, fluid exposure, and sealing level
- Interface compatibility: correct FAKRA Z coding, SMA type, and connector gender
- Manufacturing validation: continuity, impedance, and insertion-loss testing
From a technical standpoint, the FAKRA-Z-to-SMA cable is more than an accessory; it serves as a complete RF subsystem. If system specifications are not adequately defined, this will affect positioning accuracy, network stability, and the reliability of automotive wireless systems over time.
Frequently Asked Questions
What engineering problems do FAKRA Z to SMA cables solve?
The vehicles also benefit from a consistent, reliable connection between their antennas and RF modules, enabling transmission of GPS, cellular, and telematics data under harsh conditions.
Are FAKRA-Z-to-SMA cables suitable for 5G automotive platforms?
Yes. Appropriately designed, validated, and tested to meet automotive 5G specifications (sub 6 GHz), automotive antenna/RF module assemblies are essential for automotive 5G systems because they provide shielding effectiveness, vibration resistance, and low insertion loss.
Related Automotive Interconnect Solutions
- RF Cables vs. HDMI Cables: Which One Suits Your Needs?
- Introduction to RF Cable Assemblies
- RF Connector Basics: A Comprehensive Guide for High-Frequency Applications
- FAKRA Connectors: The Cornerstone of Modern Automotive Connectivity
Conclusion
FAKRA Z-to-SMA cables are an essential connector for all automotive electronic devices to standard vehicle antenna interfaces. They provide a critical RF link between vehicle antennas and RF modules for high-performance wireless systems or testing platforms. This can ultimately affect the functionality of wireless systems, as they enable a true RF path between these components.
Additionally, treating them as engineered RF assemblies rather than simple adapters provides a strong foundation for stable navigation, connectivity, and intelligent vehicle platforms.

Apple Liu is Romtronic’s Marketing Manager, focusing on business growth across the Asian market. With a background in International English and eight years of sales experience in the electronic cable and harness industry, she brings both in-depth industry knowledge and a global outlook to her role.
In addition to leading market strategy, Apple also oversees content development and editorial work—crafting clear, engaging messaging that reflects Romtronic’s values and technical strengths. She is passionate about digital engineering and is committed to strengthening Romtronic’s brand presence and innovation in a competitive global landscape.


