Analog phone jacks (modular connectors) link telephones, modems, and PBX systems over POTS lines. Common types include RJ11, RJ14, RJ25, and handset jacks like RJ9. Understanding these phone jack types (pin count and line capacity) is key in telecom cabling design.
RJ11 (6P2C/6P4C) – Single-Line Jack
Imagine plugging a standard telephone into a wall socket, typically an RJ11 connector. RJ11 is a 6-position modular jack with two active pins (6P2C) carrying one analog line. It’s the everyday connector for landline phones, analog modems, and DSL filters.

- Physical: 6P2C (two-wire) or 6P4C (four-wire) connector.
- Use: Single-line phones, analog modems, and DSL connections.
- Wiring: Twisted pair cable; center pins carry tip and ring.
- Compatibility: Fits any 6P jack. RJ11 plugs can plug into RJ14/RJ25 sockets.
RJ14 (6P4C) – Two-Line Jack
Do you need two phone lines on one plug? RJ14 is a 6P4C connector that carries two separate analog lines. It looks like an RJ11 jack but has four active pins. You’ll find RJ14 on two-line office phones and small business lines.
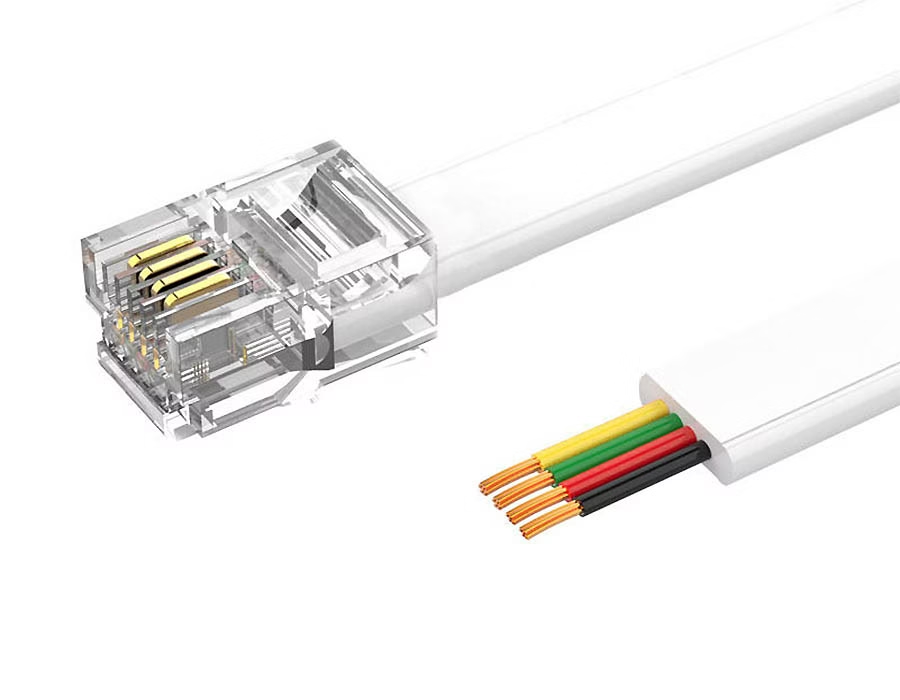
- Physical: 6P4C (four-wire) modular connector.
- Use: Two-line office phones and telephony equipment.
- Wiring: Two pairs of wires (line 1 and line 2).
- Compatibility: Fits any 6P socket. RJ14 plugs fit RJ25 jacks (extra contacts unused).
RJ25 (6P6C) – Three-Line Jack
Need three lines? RJ25 is the 6P6C jack that handles three phone lines. It fills all six contacts with three wire pairs. You’ll see RJ25 on multi-line office phones and PBX extensions.
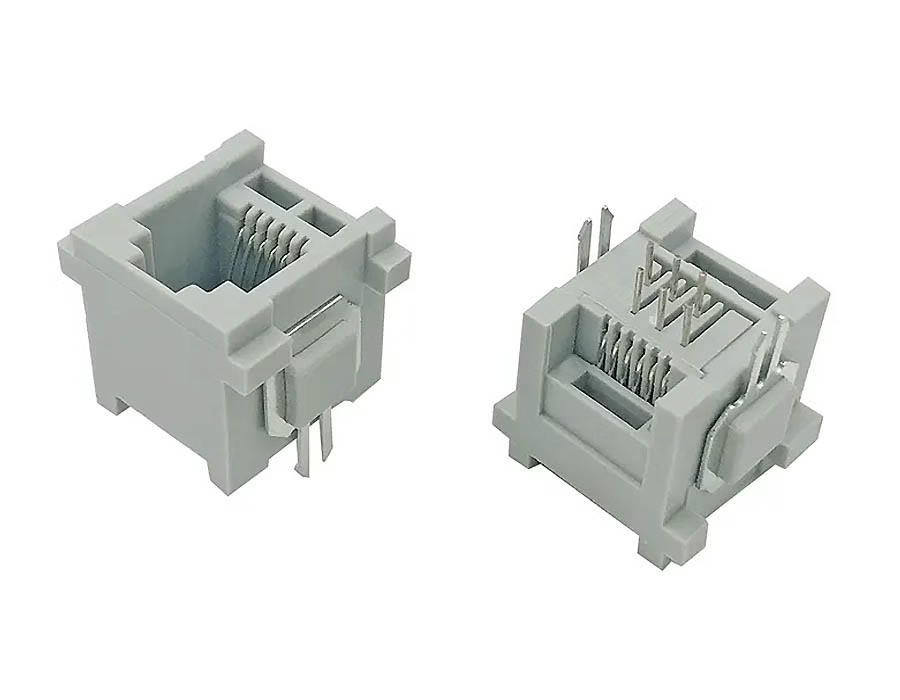
- Physical: 6P6C (six-wire) connector.
- Use: Multi-line office/PBX phones (supports up to 3 lines).
- Wiring: Three pairs of wires for lines 1, 2, and 3.
- Compatibility: RJ25 jacks accept RJ11 and RJ14 plugs (extra plug contacts unused).
RJ9 (4P4C) – Handset Connector
And for the handset cord, there’s RJ9: a 4P4C jack that connects a phone’s handset to its base. It’s not used for line-side connections. RJ9 (also called RJ10/RJ22) is found on the coiled cord linking the handset to the phone body.

- Physical: 4P4C (four-wire) mini connector.
- Use: Handset cords on phones.
- Wiring: Carries handset tip and ring (two conductors; unused filler pins).
- Compatibility: Unique 4P socket. RJ9 plugs only fit handset jacks, not standard wall jacks.
Comparing Analog Phone Jack Types
| Jack Type | Pin Count | Lines Supported | Use Case | Compatibility |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| RJ11 | 6P2C / 6P4C | 1 line | Landline phones, modems | Fits 6P jacks (RJ11/RJ14/RJ25) |
| RJ14 | 6P4C | 2 lines | Two-line office phones | 6P socket; RJ11 plugs fit (2 extra contacts unused) |
| RJ25 | 6P6C | 3 lines | Multiline PBX/office phones | 6P socket; RJ11/RJ14 plugs fit (extra contacts unused) |
| RJ9 | 4P4C | 1 (handset) | Handset cords on phones | 4P socket; not compatible with 6P jacks |
Each jack follows standard pin wiring, so lines map correctly to tip/ring pairs. For example, RJ14 assigns two lines to the middle four pins, while RJ25 uses all six for three lines. Matching the jack type to the cable wiring is essential for reliable analog voice connections.
Custom Phone Jack Solutions
Romtronic manufactures wire harnesses and cable assemblies in its factory. We manufacture custom telephone jack assemblies (RJ11, RJ14, RJ25, RJ9) and cabling solutions for analog telephone networks and PBX systems. Our in-house manufacturing ensures the reliability of cables and connectors used in commercial telecommunications infrastructure.
.avif)
Sam Wu is the Marketing Manager at Romtronic, holding a degree in Mechatronics. With 12 years of experience in sales within the electronic wiring harness industry, he manages marketing efforts across Europe. An expert in cable assembly, wiring harnesses, and advanced connectivity solutions, Sam simplifies complex technologies, offering clear, actionable advice to help you confidently navigate your electrical projects.


